From Skills to Signals: Why the Anatomy of a Microcredential Matters
We are in the midst of a meaningful shift toward skills based practices in education and workforce development. Across higher education, employers, and policy conversations, there is growing recognition that what learners know and can do matters just as much as where or how they learned it.
Microcredentials and microcredential pathways are often positioned as one of the most promising ways to make skills visible, portable, and relevant. They can help learners signal competencies, help employers understand capabilities, and help institutions respond more quickly to changing needs. But what is sometimes lost in the enthusiasm is that a microcredential is not a single artifact. It is the result of a thoughtful process.
Behind every badge is a journey.
A microcredential does not begin with a badge image or a line of metadata. It starts with an idea. Sometimes that idea comes from faculty who see a gap in their curriculum. Sometimes it comes from employers who are struggling to articulate the skills they need. Sometimes it comes from learners who want clearer pathways and recognition for learning that already exists. From that initial spark, the work unfolds through a series of deliberate steps.
Those steps often include defining the purpose and audience, aligning with industry and workforce partners, identifying skills and competencies, designing learning experiences, creating assessments, selecting platforms for delivery, and ultimately issuing a credential that is meaningful and verifiable. Each step involves decisions, tradeoffs, and collaboration.
At the heart of all of this work are skills themselves. Defining skills clearly, supporting learners as they develop those skills to a stated level of proficiency, and verifying mastery through meaningful assessment are paramount. Without shared definitions, without clarity around proficiency, and without trusted methods for validation, skills remain vague claims rather than reliable signals.
And no one does this work alone.
Microcredential development sits within an ecosystem. Faculty bring disciplinary expertise and pedagogical insight. Institutions bring governance, infrastructure, and support. Employers bring clarity around skills and relevance. Technology platforms enable content creation, delivery, assessment, and recognition. Learners are at the center, navigating all of it.
Because of this complexity, I often find myself wishing there were a simple way to explain how a microcredential comes to life without oversimplifying the work.
Recently, I was invited by Pressbooks to create a training for their team on the anatomy of a microcredential, from concept to award. They asked for something accessible and engaging, at the level of Schoolhouse Rocks classic “I’m Just a Bill”, but without the singing and dancing (they must have known I have no musical talent).
I loved the request.
So I leaned into the spirit of it.
The result was not only a comprehensive training session that walked through each stage of microcredential development, but also something a little unexpected. Using generative AI tools, specifically ChatGPT for writing and Suno for music, I created an original song, I’m Just A Skill, that tells the story of a skill on its journey to becoming a microcredential. It follows the path from idea, to alignment, to content, to assessment, to issuance. It is playful, quite accurate, and intentionally designed to make a complex process feel approachable. While the song playfully begins with “just a skill,” the reality is that skills are foundational. They are the building blocks upon which microcredentials, pathways, and skills based practices are built.
The song opens the training, sets the tone, and reminds us that even serious systems benefit from a bit of creativity. It also reinforces an important point. If we want skills based practices to scale and succeed, we need shared understanding. We need tools and platforms that support the full lifecycle of a microcredential, not just the final badge. And we need ways to bring diverse stakeholders into the conversation early and often.
For me, this work continues to be about connection. Connecting learning to work. Connecting ideas to outcomes. Connecting people across institutions, industries, and technologies. Microcredentials are one way we make those connections visible, but only when we respect the process and the ecosystem that make them possible.
You can listen to the song here and follow along with the journey from skill to signal. I hope it makes you smile and maybe helps clarify why the anatomy of a microcredential matters.
Note:
The song referenced in this post was created using generative AI tools, specifically ChatGPT for lyric development and Suno for music generation. These tools were used as creative collaborators, not replacements for human judgment, expertise, or values. The content, structure, and learning goals were intentionally designed to fairly accurately reflect the microcredential development process and to support understanding through storytelling. In the spirit of openness and transparency, I believe it is important to name when and how AI is used, especially in educational and creative contexts, and to model thoughtful, ethical, and purposeful use of these emerging tools.
“I’m Just a Skill (The Anatomy of a Microcredential)” by Dr. Lisa C. Young, licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Exploring the Badge Summit’s Petting Zoo: A Student-Eye View into the LER Ecosystem
Images from the Badge Summit at CU Boulder. Lisa Young and Andrew Fisher recording a podcast while playing Connect4 and earning an open digital badge.
When I visit a traditional petting zoo, my favorite part is watching children interact with the animals—the unfiltered wonder, curiosity, and, occasionally, trepidation. That raw, genuine reaction is what I carried with me into the Badge Summit’s Petting Zoo. This time, however, I deliberately chose to experience the event through the lens of a student navigating the emerging landscape of digital credentials and interoperable learning systems. And just like at a real petting zoo, I encountered awe, discovery, and a little bit of uncertainty.
From the outset, I was excited. This was a rare opportunity to engage hands-on with the very ecosystem I work within—a space that blends digital credentials, metadata frameworks, skills-based hiring, and credential wallets. My journey began by creating a SmartResume account and importing the digital badges and verified credentials I had previously earned. It was gratifying to revisit my accomplishments—not merely as a static list, but as dynamic data assets enriched with metadata about competencies, issuing institutions, and pathways.
Much like a student entering a new learning environment, I felt a mixture of enthusiasm and apprehension. Just as children eagerly search for their favorite animals at a petting zoo, I set out to discover new badges and microcredentials I could earn. Various exhibitors and educational organizations offered opportunities—from scanning QR codes at booths to participating in meaningful learning interactions. One highlight was recording a podcast with Andrew Fisher from Bristol Community College over a spirited game of Connect4. (I even won, though I needed a nudge to recognize it had happened—clearly, it had been a while!) This part of the experience brought a renewed sense of wonder as I witnessed firsthand the interoperability of these credentials and how they flowed into my wallet.
Interoperability, in the LER ecosystem, is more than convenience—it’s foundational. The ability to ingest credentials from disparate sources into a unified learner record, and to leverage them across platforms like SmartResume, LinkedIn, and others, is central to achieving true learning mobility. This is where the ecosystem becomes transformative: badges and records are not isolated tokens but part of an interconnected web of skills evidence, aligned to frameworks and employer needs.
As I continued to build out my SmartResume, integrating both my newly earned and historical credentials, I appreciated how the platform's AI functionality supported me in articulating job experiences and skills. This mirrors the experience we want for students—technologies that not only store achievements but help make meaning of them. The SmartResume’s ability to synthesize my work history, education, and verified credentials into a coherent, skills-aligned profile was an invaluable reflection point. It’s easy to see how learners can begin to understand their own learning journeys and career pathways when presented through a structured, interoperable lens.
Yet, just like in any new learning environment, I encountered some challenges. From a student perspective, one of the most frustrating aspects was the fragmentation of credentials across multiple wallets and issuers. With various login credentials and platforms, it’s easy to overlook or lose track of what you've earned—particularly when different systems don't yet speak fluently with each other. Despite this, I was encouraged by the visible progress in interoperability efforts. It’s a reminder that while the LER ecosystem is still in development, we are well on our way toward a more learner-centered, skills-transparent future.
My sincere thanks go to Noah Geisel, the Badge Summit team, and all the participating partners who brought the Petting Zoo to life (SmartResume, Territorium, Gobekli, Bristol Community College, LearnCard, Accredible, and so many more). Their willingness to showcase tools in such a hands-on, experimental space reflects the kind of bold vulnerability and openness the ecosystem needs as we co-develop standards, governance, and best practices.
Just like a student stepping into a vibrant new campus environment, I left the Petting Zoo with my curiosity piqued, my portfolio enriched, and a deeper understanding of the technical and human sides of digital credentialing. I hope this becomes a recurring part of future summits—it’s exactly the kind of interactive, learner-focused engagement that moves this work forward.
Feel free to explore my SmartResume here (note: still a work in progress!).
Where Microcredentials and Open Can Intersect: A Framework
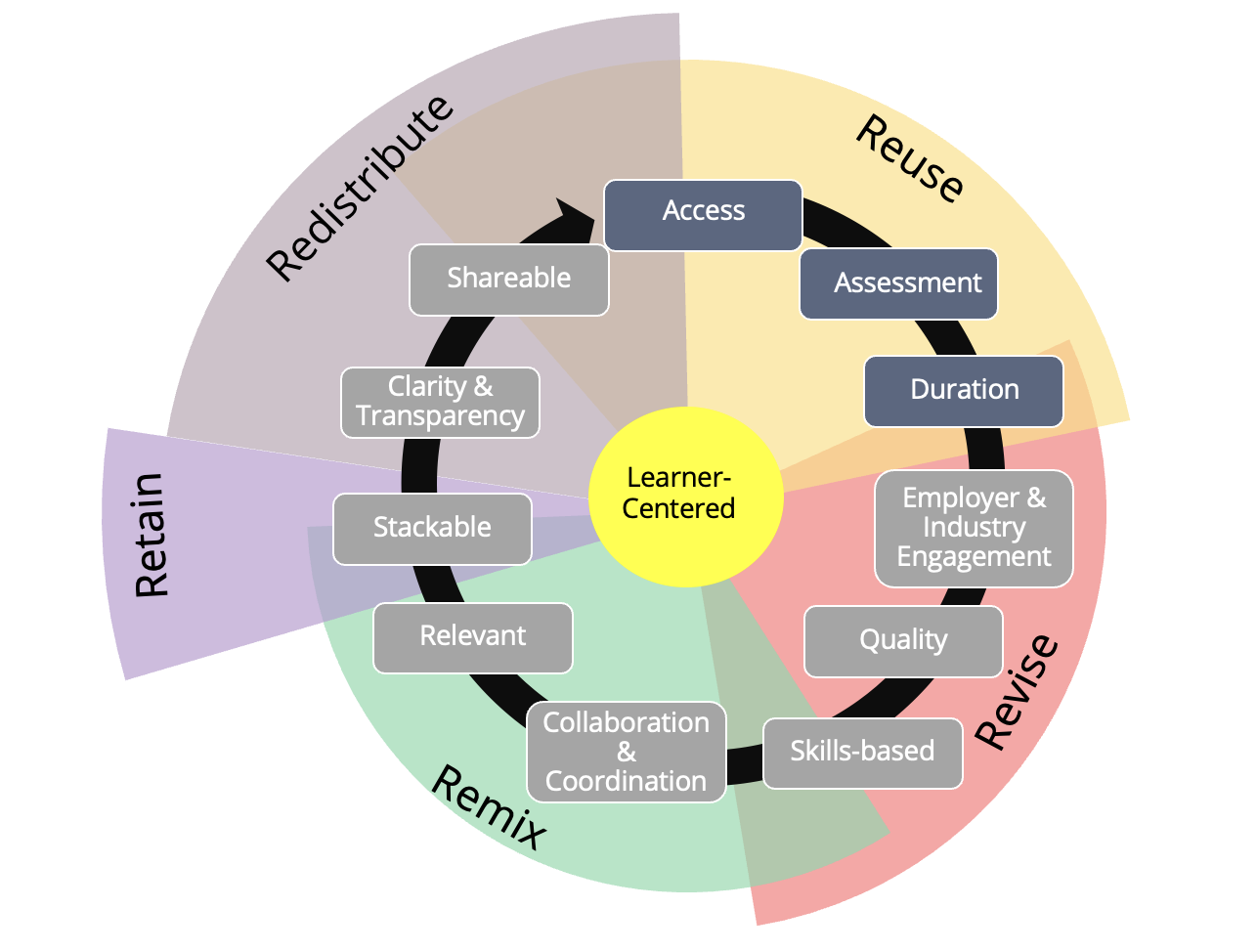
At the edges of education, innovation often begins not with sweeping mandates, but with small, intentional shifts that challenge tradition and expand possibility. Microcredentials have emerged as one of those shifts, blurring the lines between formal education and workforce readiness, between classroom theory and real-world application. When combined with the principles of Open Educational Resources (OER), microcredentials can evolve into powerful tools for equity, flexibility, and lifelong learning. This post explores how integrating the 5Rs of Open Education, Revise, Remix, Retain, Redistribute, and Reuse, into the microcredential framework I shared in my prior post can help reimagine credentialing at the outer edges of what is possible in higher education.
The 5Rs of Open Education form the foundation of OER’s transformative power (Wiley, 2014). They grant users the legal and pedagogical freedom to:
· Retain (keep copies of content),
· Reuse (use the content in a variety of ways),
· Revise (adapt or modify the content),
· Remix (combine content with other materials to create something new),
· Redistribute (share copies with others).
"5Rs of OER " image by Jonathan Dhyr is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
These permissions are enabled through open licensing, typically Creative Commons licenses, that empower educators, institutions, and learners to actively shape their educational experiences, rather than passively consume them. When integrated into microcredentials, the 5Rs support a culture of adaptability, innovation, and inclusivity.
An Open Microcredential Framework
Access becomes more inclusive when OER is at the foundation. By reusing openly licensed content, institutions can reduce financial barriers for learners. Redistributing those materials widely ensures that non-traditional learners—such as working adults, incarcerated students, and underserved populations—can participate in meaningful learning experiences tailored to their contexts.
Assessment methods also benefit from OER. Instructors can reuse open-source tools and simulations. Competency-based learning becomes more achievable when assessments are adaptable and freely available.
Duration becomes more flexible with reusable, modular OER content that can be adapted to suit a variety of learning formats and timelines. Educators can revise these open materials to shorten, expand, or reconfigure learning experiences based on the needs of specific learner groups or program goals. This adaptability supports the creation of short, stackable microcredentials that align with evolving industry demands while accommodating learners’ varying schedules and commitments.
Employer and industry engagement is enhanced when OER allows for iterative, agile content development. Industry partners can help revise and shape content, ensuring it reflects current job roles and technologies. Co-creation of OER with employers makes credentials more trustworthy, practical, and valuable in the labor market.
Quality remains paramount, and OER supports it by enabling faculty and industry experts to revise content to meet specific competency needs. Regular peer review of open materials ensures alignment with both academic rigor and real-world application.
Skills-based education is further strengthened through OER by allowing instructors to revise and remix materials that map directly to skills. This approach supports a personalized experience that accommodates various learning styles and paces.
Collaboration and coordination are natural outcomes of an open ecosystem. When institutions remix and co-create OER, they share responsibility and reduce redundancy, resulting in more robust, targeted microcredentials. Shared repositories and open collaboration will make it easier to scale efforts across systems and sectors.
Relevance thrives through the remixing of OER. As labor market needs evolve, educators can continuously adapt and combine content to stay aligned with emerging skills and technologies. This flexibility allows for localization, ensuring that credentials remain aligned with regional economic needs and career opportunities.
Stackability is a hallmark of effective microcredentials, and OER plays a key role. Through remixing and layering of foundational and advanced content, learners can build meaningful pathways to degrees or professional certifications. Meanwhile, the ability to retain OER materials supports lifelong learning and skill refinement.
Clarity and transparency are strengthened through redistribution. Publishing OER-based competencies, outcomes, content, and assessments allows learners and employers to understand what a microcredential represents before, during, and after enrollment.
Shareability is embedded in the nature of OER. Learners can redistribute digital badges and OER-based credentials across platforms like LinkedIn and digital portfolios. These credentials, and the knowledge behind them are portable, verifiable, and easily integrated into professional networks. Further, shareable microcredentials rely on more than just the visibility of digital badges, they also depend on the openness of the content behind them. By leveraging OER, institutions can redistribute not only the credentials but also the underlying learning materials, making both accessible to a broader audience. This transparency allows learners and employers to see exactly what skills and competencies have been developed. Additionally, OER content can be reused across platforms and programs, supporting consistent messaging and broader dissemination of both learning outcomes and instructional materials. These practices enhance the portability, credibility, and value of microcredentials in both academic and professional settings.
And…. most importantly, Learner-centered design is at the heart of both the microcredential framework and the 5Rs of open education. Together, they empower learners to take ownership of their educational journeys by offering flexible, relevant, and accessible pathways. The microcredential framework ensures that learning is aligned with real-world skills, supported by industry engagement, and adaptable in duration and format. Meanwhile, the 5Rs—Revise, Remix, Reuse, Redistribute, and Retain—equip educators and learners with the tools to personalize content, update materials to reflect evolving goals, and share knowledge widely. This synergy fosters an inclusive environment where learners can engage with meaningful, tailored experiences that directly support their aspirations, career growth, and lifelong learning.
Acknowledging the Challenges of Open Microcredentials
Despite the many benefits, integrating OER into microcredentialing also presents challenges that must be thoughtfully addressed. One concern is consistency. As materials are revised and remixed across institutions and instructors, the risk of variation in content and assessments increases. This lack of uniformity can create confusion for employers attempting to interpret the value of a microcredential and assess what specific skills or knowledge a learner has mastered. Additionally, if quality assurance processes are not rigorously upheld, the integrity of content and assessments may be diluted, potentially undermining trust in the credential itself. This could lead to a diminished reputation of open microcredentials in the labor market, where employers may perceive them as less reliable or verifiable than traditional credentials. Maintaining academic and industry alignment, while still allowing for the freedom and creativity that OER encourages, requires intentional governance, transparent standards, and cross-sector collaboration.
The Future is Open and Learner-Centered
At the edges of education, we find room to question, adapt, and invent. The integration of OER into microcredentials is not without complexity—but that complexity is where meaningful transformation lives. As we rework systems to better serve diverse learners and rapidly evolving industries, open microcredentials offer a model that is scalable, affordable, and radically learner-centered. By anchoring this framework in openness, we honor the spirit of education as a public good—one that thrives not in silos, but in shared knowledge, co-creation, and continuous reinvention. The edge is not the end; it’s the beginning of what’s next.
A Value Framework For Microcredentials
It all begins with an idea.
For the past two decades, much of my professional journey has been rooted in the open education movement—working to expand access, lower barriers, and empower learners through affordable and flexible pathways. Recently, my focus has expanded to another exciting innovation in higher education: microcredentials.
These two passions—open education and microcredentials—both have powerful potential to reshape how we meet the needs of today’s students. While this post focuses specifically on microcredentials, I look forward to sharing future insights about how these two movements can intersect and strengthen each other.
About Microcredentials
Before diving deeper, it's important to define some key terms. Institutions often develop specific taxonomies for microcredential work, but for this conversation, I'll highlight three foundational definitions: microcredentials, microcredential pathways, and open digital badges.
At their core, microcredentials are credentials that verify, validate, and attest that specific skills and/or competencies have been achieved. Unlike traditional degrees and certificates, microcredentials are generally offered in shorter or more flexible timespans and tend to focus more narrowly on specific skills or areas of expertise.
A microcredential pathway links two or more microcredentials together, creating a road map that offers students an off-ramp to a livable wage and an onramp to stackable credentials. These pathways are intentionally designed to help students achieve meaningful milestones while also keeping the door open to further academic and career advancement.
Taking this further: I like to think that microcredentials and pathways are student-centered, industry-driven, and faculty-powered. We must value our faculty expertise while collaborating with industry partners to validate the skills embedded in each microcredential, ensuring that students are gaining expertise that leads directly to real-world opportunities. Our designs must emphasize mastery of skills at defined proficiency levels—often higher than the baseline expectations of a course—and we must ensure both credit and non-credit pathways align with broader academic certificates and degrees.
An essential part of this ecosystem is the open digital badge—a digital representation of a microcredential or microcredential pathway. Open digital badges contain rich metadata describing the skills mastered, earning criteria, and expiration information, and they align with widely recognized skills databases. Students can showcase these badges in their Learner Employment Record (LER) and share them across professional and social platforms, creating a dynamic, portable record of achievement.
Image from 1EdTech, retrieved from https://www.1edtech.org/clr/faq on April 26, 2025.
The Value Proposition of Microcredentials
Microcredentials offer tangible value across the educational landscape—benefiting students, institutions, and industry alike. Their short-term, targeted nature addresses urgent needs while creating new possibilities for long-term growth.
For Students:
Targeted Learning: Microcredentials provide focused and relevant learning experiences in specific fields.
Enhanced Competitiveness: They boost learners’ marketability and distinguish them in competitive educational and employment environments.
Flexibility: Students can balance learning with work and other commitments, progressing at their own pace.
Industry Alignment: Learners gain expertise that aligns with current and emerging industry needs.
Recognition: Microcredentials offer formal, verifiable recognition of skills that can be immediately shared with employers.
For Higher Education Institutions:
Curriculum Agility: Institutions can rapidly respond to evolving workforce needs by offering specialized, stackable learning opportunities.
Industry Collaboration: Microcredentials strengthen ties with industry partners, ensuring educational relevance and impact.
Attracting Diverse Learners: Microcredentials appeal to working adults, career changers, and others seeking skill-based education.
For Industry:
Workforce Readiness: Employers gain access to a pipeline of workers with verified, job-relevant skills.
Skills Verification: Microcredentials provide a trusted signal of employee capabilities.
Talent Development: Organizations can upskill or reskill employees efficiently, supporting innovation and adaptability.
Expanded Talent Pools: Industries tap into broader networks of qualified professionals, strengthening workforce resilience.
Microcredential and Pathway Design Considerations
The Education Design Lab (the Lab) is a national nonprofit that co-designs, prototypes, and tests education-to-workforce models through a human-centered design process focused on understanding learners’ experiences, addressing equity gaps in higher education, and connecting learners to economic mobility (EDL, 2025).
EDL has established design criteria for microcredential pathways. The Eight EDL design criteria guide the development of learner-centered programs that connect education to employment. Using the EDL design criteria, microcredential pathways should feature two or more stackable and portable credentials that seamlessly build toward other credentials which can include a degree, allowing learners to progressively advance their education and careers. Each credential will be directly aligned with dynamic regional labor market trends, employment needs, and wage data to ensure strong workforce relevance. The design will be employer-initiated and validated to guarantee the skills taught meet real-world demands. Learners will complete each credential in one year or less through flexible delivery formats—online, hybrid, and in-person—providing accessible pathways for diverse populations. The program will be intentionally affordable and digitally discoverable to maximize visibility and equity. It will integrate both technical skills and essential 21st-century durable skills, ensuring graduates are equipped to succeed and adapt in an evolving workforce.
Education Design Lab (EDL) Design Criteria. Retrieved from https://eddesignlab.org/areas_of_work/designing-for-new-majority-learners/ on April 26, 2025.
The Microcredential Value Framework
This learner-centered microcredential value framework is built on the principles of access, quality, relevance, collaboration, employer engagement, clarity, flexibility, and meaningful assessment. Access is prioritized by ensuring microcredentials are inclusive and accessible to a diverse range of learners, including non-traditional students, working professionals, and underserved populations. Key elements supporting access include flexible entry points with open-access pathways, low-cost or free learning materials leveraging open educational resources (OER), comprehensive support services such as advising and career guidance, and targeted outreach.
Quality is emphasized through rigorous development and review processes involving subject matter experts, alignment with academic and industry needs, and regular updates to maintain the relevance and integrity of offerings. Relevance ensures that microcredentials are directly linked to market needs and emerging industries, incorporating employer-desired soft skills and technical skills competencies, and remaining adaptable to technological and workforce shifts through ongoing industry consultation.
Collaboration and coordination are key to fostering partnerships between educational institutions, employers, and industry bodies for the co-creation of microcredentials. Cross-institutional collaboration supports credit portability, and engagement with professional associations and community organizations expands access and co-delivery opportunities. Employer and industry engagement is central to this framework, involving employers in the design, validation, and endorsement of microcredentials, ensuring real-world applicability, and creating pathways for work-based learning such as internships and apprenticeships.
A commitment to clarity and transparency provides learners and employers with detailed information about competencies, assessment methods, credential duration, and career pathways. Clear articulation of value, standardized language, and transparent frameworks help learners make informed decisions. The duration of microcredentials is designed to be flexible, offering short, intensive learning experiences, self-paced options, and a variety of formats including boot camps, workshops, and online modules to fit diverse learner needs.
Robust assessment practices focus on skills-based evaluations that require demonstration of skills and knowledge through portfolios, projects, and simulations aligned with industry standards. Microcredentials are intentionally stackable, allowing learners to build towards larger qualifications such as degrees or professional certifications, facilitating both vertical and horizontal progression across disciplines. A skills-based approach, rather than traditional seat-time models, ensures that learners advance upon mastery of clearly defined skills and competencies, supported by performance-based assessments.
Finally, microcredentials are designed to be shareable, portable, and verifiable, with digital badges or certificates that integrate with platforms such as LinkedIn or blockchain-based credentialing systems. Clear metadata highlights the specific skills, competencies, and achievements for academic and employer recognition. Altogether, this learner-centered framework ensures that microcredentials provide accessible, high-quality, relevant, and empowering educational opportunities that align closely with both learner goals and workforce demands.
Microcredential Value Framework
Microcredentials live at the frontier of educational innovation, offering new ways for learners to access opportunity, prove their skills, and accelerate their careers. They challenge us to think differently about what success looks like—and to design systems that are more flexible, inclusive, and responsive to the real world.
As we continue to work at the edges of education, where creativity and purpose drive transformation, microcredentials offer us a powerful way forward. They represent not just smaller credentials—but bigger opportunities: to empower students, strengthen institutions, and fuel industries with the talent they need for the future.
This is the work of those who believe in the innovative edge of teaching and learning—and I’m excited to continue exploring it with you.